Air cooled condensers play a critical role in industrial cooling and heat rejection systems. As industries continue to seek energy-efficient, water-conserving, and environmentally responsible cooling solutions, air cooled condensers have become a preferred choice across many sectors. From power generation and petrochemical processing to HVAC and refrigeration, these systems provide reliable performance without the heavy water dependency associated with water cooled alternatives.
This article explores the major types of air cooled condensers used in industrial applications, explaining their design principles, operational characteristics, and suitability for different operating environments.
An air cooled condenser is a heat exchange device that removes heat from a working fluid by transferring it to ambient air. Instead of using water as the cooling medium, these systems rely on airflow generated by fans or natural convection. The heated vapor or gas inside the condenser is cooled, condensed, and returned to the system for reuse.
Industrial air cooled condensers are engineered to handle high pressures, elevated temperatures, and continuous operating conditions. Their robust construction and adaptability make them suitable for both small-scale installations and large industrial plants.
Air cooled condensers are widely used in industries where water availability is limited or water conservation is a priority. They reduce operational complexity by eliminating cooling towers, water treatment systems, and wastewater management.
In addition, these condensers offer easier installation, lower maintenance requirements, and improved environmental compliance. Their modular designs allow scalability, making them ideal for industries with expanding capacity requirements.
Industrial air cooled condensers are classified into different types based on their construction, airflow arrangement, and operational requirements. Each type is designed to address specific industrial challenges and environmental conditions.
Horizontal air cooled condensers are among the most commonly used designs in industrial applications. In this configuration, finned tubes are arranged horizontally, and fans are positioned either above or below the tube bundles to force air across the heat transfer surface.
This type of condenser is widely used in power plants, refineries, and large HVAC systems due to its simple design and ease of maintenance. The horizontal layout allows for effective airflow distribution and accommodates large heat rejection capacities.
Horizontal air cooled condensers are particularly suitable for installations where space is available and where consistent airflow can be maintained throughout operation.
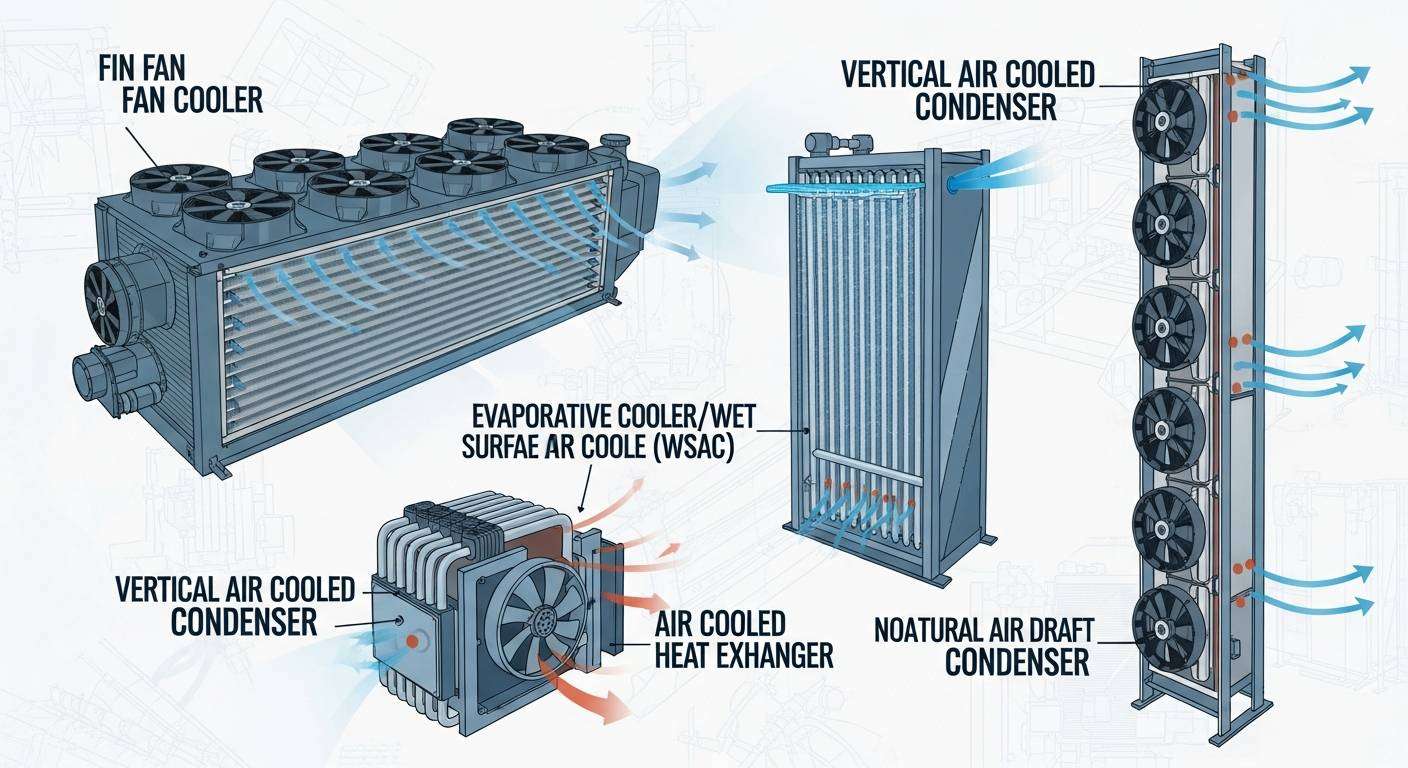
Vertical air cooled condensers feature vertically oriented tube bundles with airflow moving horizontally or vertically across the fins. This design is often selected when ground space is limited or when specific airflow patterns are required.
In industrial settings, vertical air cooled condensers are commonly used in chemical processing plants and modular cooling systems. Their compact footprint allows for installation in confined areas while maintaining efficient heat transfer performance.
Vertical designs are also beneficial in dusty or debris-prone environments, as their orientation can reduce fouling on fin surfaces.
A-frame air cooled condensers are named for their distinctive A-shaped structure. In this configuration, two sloped tube bundles are arranged in an inverted V shape, with fans positioned beneath them to draw air upward through the fins.
This type of condenser is extensively used in power generation and large industrial processes. The A-frame design offers excellent structural stability, uniform airflow distribution, and high thermal efficiency.
A-frame air cooled condensers are especially effective in high-capacity applications where large volumes of heat must be rejected continuously under varying ambient conditions.
Forced draft air cooled condensers use fans located at the air inlet to push ambient air across the condenser surface. The airflow is driven directly through the finned tubes, allowing precise control over cooling performance.
In industrial environments, forced draft condensers are preferred when airflow direction and velocity need to be carefully managed. These systems are often used in enclosed installations or areas with strict noise control requirements.
Forced draft designs are relatively easy to service, as fans are positioned at ground level, simplifying inspection and maintenance tasks.
Induced draft air cooled condensers operate with fans positioned at the air outlet, pulling air through the condenser rather than pushing it. This configuration helps achieve more uniform airflow across the heat transfer surface.
Industrial applications favor induced draft condensers for their superior thermal efficiency and reduced risk of hot air recirculation. These systems are commonly installed in outdoor environments where wind conditions may affect airflow patterns.
Induced draft air cooled condensers also tend to have lower operating noise at ground level, making them suitable for facilities with noise sensitivity concerns.
Natural draft air cooled condensers rely on buoyancy-driven airflow rather than mechanical fans. As hot air rises, cooler ambient air is drawn through the condenser, enabling heat rejection without additional energy input.
While less common in modern industrial installations, natural draft condensers are still used in specific applications where energy consumption must be minimized and operating conditions allow for sufficient natural airflow.
These systems are best suited for locations with stable ambient temperatures and adequate vertical space to support natural convection.
Modular air cooled condensers are designed as self-contained units that can be combined to meet varying capacity requirements. Each module includes its own tube bundle, fan assembly, and control system.
Industries with phased expansion plans or variable cooling demands benefit from modular designs. These condensers allow capacity to be increased or decreased without major system modifications.
Modular air cooled condensers are widely used in industrial refrigeration, data centers, and manufacturing facilities where flexibility and scalability are critical.
Steam air cooled condensers are specialized systems used primarily in thermal power plants. They condense exhaust steam from turbines using ambient air, eliminating the need for large quantities of cooling water.
These condensers are engineered to handle high steam flow rates and large heat loads. Their design often incorporates A-frame structures and induced draft fans to maximize efficiency.
Steam air cooled condensers are particularly valuable in arid regions or locations with strict water usage regulations.
Refrigerant air cooled condensers are used in industrial refrigeration and process cooling systems. They condense refrigerant vapor back into liquid form, enabling continuous cooling cycles.
These condensers are designed to operate efficiently under varying load conditions and ambient temperatures. Their robust construction ensures reliable performance in demanding industrial environments.
Refrigerant air cooled condensers are commonly found in cold storage facilities, food processing plants, and chemical manufacturing operations.
V-type air cooled condensers are a variation of the A-frame design, featuring a narrower angle between tube bundles. This configuration allows for compact installation while maintaining effective airflow and heat transfer.
Industrial applications that require high performance in limited space often utilize V-type condensers. Their aerodynamic design helps reduce fan power consumption and improve overall system efficiency.
The performance and durability of air cooled condensers are influenced by the materials used in their construction. Industrial condensers are commonly manufactured using carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or copper alloys.
Material selection depends on operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, corrosion potential, and environmental exposure. Proper material choice enhances service life and reduces maintenance costs.
Different industries require different types of air cooled condensers based on their process requirements. Power plants prioritize high-capacity steam condensers, while petrochemical facilities focus on corrosion-resistant designs.
Food processing and pharmaceutical industries often require hygienic designs and precise temperature control. Understanding application-specific needs is essential for selecting the most suitable condenser type.
Several factors influence the choice of air cooled condenser in industrial applications. Ambient temperature, heat load, space availability, noise limitations, and energy efficiency targets all play a role in selection decisions.
Proper system design ensures optimal heat rejection while minimizing operating costs and environmental impact.
Air cooled condensers offer significant advantages over water cooled alternatives, particularly in terms of water conservation and reduced environmental footprint. They simplify plant infrastructure and lower long-term maintenance requirements.
Their adaptability and modularity make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, from small manufacturing plants to large power generation facilities.
Despite their benefits, air cooled condensers also face certain limitations. Performance can be affected by high ambient temperatures, and larger footprints may be required for high-capacity installations.
Careful design and proper selection help mitigate these challenges and ensure reliable long-term operation.
Advancements in materials, fan technology, and control systems are shaping the future of air cooled condensers. Improved fin designs, variable speed fans, and smart monitoring systems are enhancing efficiency and reliability.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, air cooled condensers are expected to play an increasingly important role in industrial cooling strategies.
Air cooled condensers are essential components in modern industrial cooling systems, offering efficient heat rejection without the need for water. Understanding the different types of air cooled condensers used in industrial applications helps engineers, plant managers, and procurement teams make informed decisions.
From horizontal and vertical designs to A-frame, modular, and steam air cooled condensers, each type serves specific operational needs. Selecting the right condenser ensures optimal performance, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability, making air cooled condensers a valuable investment for industrial facilities worldwide.
Air cooled condensers play a critical role in industrial cooling and heat rejection sys
READ FULLAir-cooled condensers are significant components of most cooling sys
READ FULLA refrigerator is hard at work all day long, keeping your food cool.
READ FULL