Air-cooled condensers are significant components of most cooling systems. They assist in cooling down buildings, factories, and machines. Learning how they function helps you appreciate their heating and match them to your needs, saving energy.
An air-cooled condenser is a piece of equipment that draws the heat from the cooling system. This is done by collecting the hot gas and cooling it using air, thus it becomes liquid. It should be thought of as being like an automobile radiator, but in air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
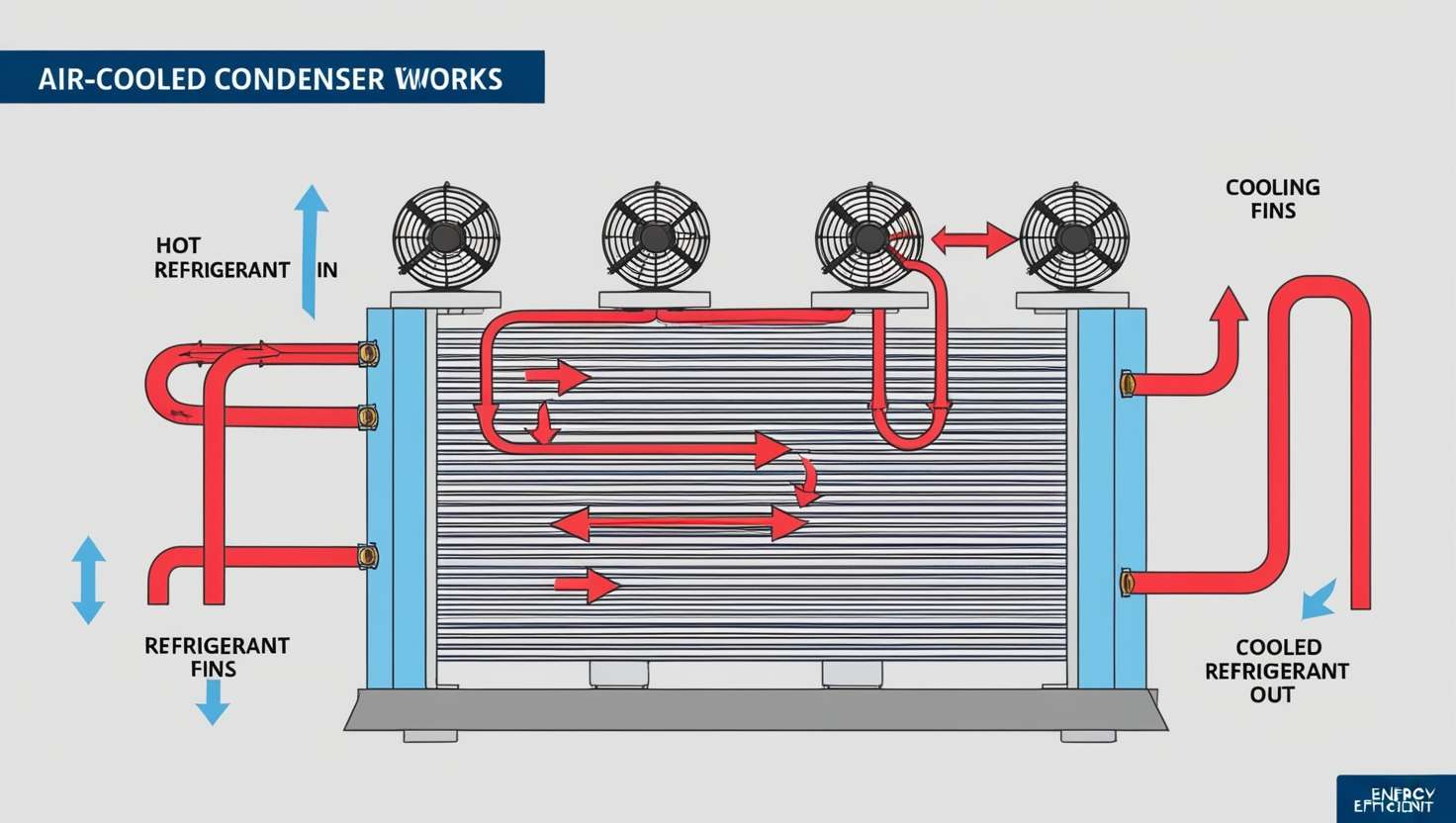
The condenser is outside buildings or on the roof. It contains metal tubes, fins, and fans that help to circulate heat away from the building. As these tubes are heated with hot gas, the air outside cools the gas to a liquid again.
Basic Process
The cooling process occurs in easy ways. First, hot gas moves in the condenser through the indoor cooling unit. This gas transports heat within your building. This gas is allowed to flow through metal tubes encased in metal thin fins.
These tubes and fins are cooled by the movement of outside air over them using large fans. The air acquires the heat as it travels over the hot tubes. The hot gas present in the tubes cools and converts to liquid. This liquid is now returned to the indoor unit to restart the cooling process.
Function of Refrigerant
The liquid and gas in the tubes are referred to as the refrigerant. This special fluid can easily transform and solidify when it is heated or cooled so as to become liquid. Refrigerant turns into a gas when it is hot. On cooling, it shrinks back into liquid.
The refrigerant picks up the heat in your building and dumps it in the outdoor condenser. After the removal of the heat, the cold liquid refrigerant is brought back inside and takes up more heat.
The Condenser Coils
The most significant part of the air-cooled condenser is the coil system. These coils are metal tubes usually comprising copper or aluminum. Hot refrigerant is carried in these tubes, and outside air is circulated through these tubes. This metal is capable of handling heat; therefore, the hot refrigerant loses the heat to the outside colder air.
Fans and Motors
Large fans blow over the condenser coils. These fans are operated using electricity-powered motors and aid in accelerating the process of heat transfer. Unless the condenser has the right airflow, it cannot dislodge the heat efficiently. Depending on size, the majority of condensers contain one or more fans.
The Compressor
The compressor is often referred to as the heart of the system. It circulates the refrigerant through the whole cooling system. The compressor compresses the gas from low pressure to high pressure. The process heats the refrigerant, and this assists in drawing heat from the condenser.
Fundamentals of heat transfer
Heat never goes anywhere except that which is hot to the cooler. Hot refrigerant behind coils of the air-cooled condenser sheds its heat into cooler outside air. This metal coil is effective in facilitating such a transfer of heat through its coil.
The Role of Airflow
Heat can be transported out more easily with moving air than with still air. That is why there are fans in condensers to move air over the coils. Heat can be removed from the condenser more quickly when the air passes through it. This is similar to why you feel cooler when there is a fan blowing on you.
The temperature difference is significant
The greater the amount of the temperature difference between the hot refrigerant and the outside air, the more rapid is the transfer of heat. Therefore, air conditioning appliances work more effectively when the outside is not hot. On very hot days, it takes more work to extract the same amount of heat with condensers.
Split System Condensers
Home and small buildings are most often split system condensers. The condenser is placed outdoors, and the indoor unit is responsible for air circulation. The reason why the systems are popular is that they are pretty quiet and easy to install.
Package Unit Condensers
Package units have the two components, the condenser and the indoor unit, all in one box. The units are usually situated on building tops or adjacent buildings. They are suitable for bigger areas and are less demanding because all components are contained in a single place.
Modular Condensers
Modular condensers include several smaller condensers that work together. Such a layout is easier to control and may be more efficient on large constructions. In case one of the modules needs repair, other modules can continue performing.
Less Water Consumption
Water-cooled systems being different, air-cooled condensers don’t require a continuous water supply. This qualifies them to be ideal in regions with limited water or where it is costly. They also do not cause worries of water treatment, as well as legionella bacteria.
More suitable for small buildings
Air-cooled condensers are the most feasible in small buildings. They are practical and safe in cooling with ease compared to the bigger water-powered cooling systems. This qualifies them to be in homes, small offices, and retail rooms.
Keep Clean Coils
It is not possible to transfer heat with dirty coils. Frequent cleaning of the condensers increases efficiency levels and saves a lot of energy. Leaves, dirt, and debris have to be cleared regularly to keep the proper air flow.
Sizing should be done correctly
Efficiency depends on the proper selection of the condenser size. An undersized unit will also be in a mode of continuous operation, consuming more energy. An oversized unit will not only waste energy but also will switch on and off a lot, thus decreasing comfort.
Regular Maintenance
Efficiency may be increased significantly through simple care. This involves inspection of refrigerant, cleaning or changing filters, and proper functioning of fans. Properly maintained systems have lower energy consumption and have a longer life.
Smart Controls
Advanced condensers will be able to operate intelligent thermostats and controls. These controls assist the system in running only when necessary and at optimal levels. There is a lot of energy that can be saved by programming the system to suit your particular routines during the day.
Poor Airflow Problems
Obstruction of airflow is an easy occurrence, which lowers efficiency. Other objects nearby, such as plants, fences, etc, may end up blocking air movement near the condenser. Having two feet or more of free space around the unit can keep the air flowing properly.
Refrigerant Leaks
Insufficient levels of refrigerant increase the workload of the system to consume more power. Refrigerant repairs can only be done by qualified technicians because special tools and training are needed. Small leaks are possible to identify early through regular inspection.
Fan Problems
Faulty or sluggish fans are unable to circulate air along the coils. This decreases the efficiency of heat removal by the condenser. Fans and motors need to be inspected periodically and replaced when a fan fails.
Better Efficiency Levels
New efficiency requirements are urging manufacturers to develop improved condensers. Such better units consume less power and still deliver the same cooling ability. Equipment with high efficiency can give long-term savings through investment.
Integrated smart technology
Smart features that keep track of performance and automate operations are increasingly added in modern condensers. Such systems are capable of identifying issues in advance and maximizing performance based on weather conditions and usage patterns.
Environmental Considerations
There are newer refrigerants that are being developed that have a smaller environmental impact. Air-cooled condensers have a brighter prospect as a cooling tool, along with the improved efficiency of these changes.
Air-cooled condensers are invaluable parts that render modern cooling systems possible. They operate by extracting heat from interior rooms to the open air in a straightforward yet effective way. Knowledge of how such systems operate ensures you make sound decisions regarding cooling requirements and servicing.
Air-cooled condensers are significant components of most cooling sys
READ FULLA refrigerator is hard at work all day long, keeping your food cool.
READ FULLThe evaporator supplier is highly important if you run a business th
READ FULL